Skvělý článek, dobře vysvětleno.
Technical principles of metal detectors
Categories: Metal Detectors - Reviews and Tests , Search instructions
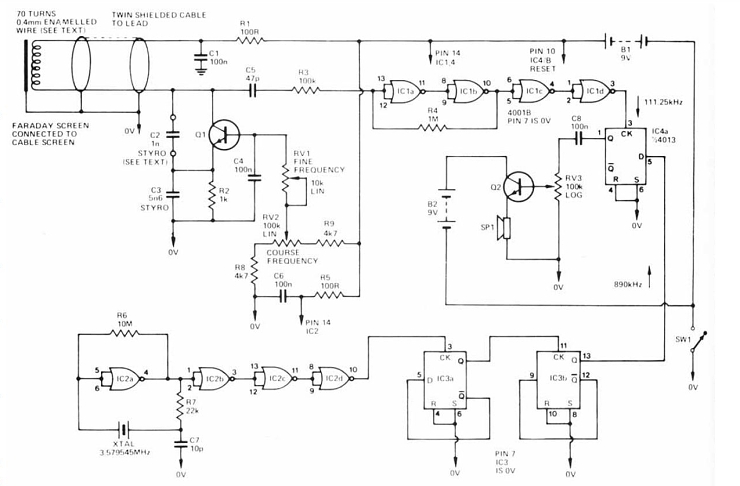
There are currently four basic principles of metal detector function. The different principles have a number of advantages and disadvantages between them. Especially in the depth of range, the ability to detect small objects, the ability to distinguish the types of metals detected and the method of use.
1) BFO detectors ( Beat Frequency Oscillator )
The main principle of this detector consists of two oscillators, one of which serves as a reference and the other oscillator (LC) is formed by a search probe to apply the change in inductance of the coil. Both oscillators oscillate in the resting state at a close frequency, and when a metal object is approached, the oscillator formed by the search coil detunes and a frequency change occurs compared to the reference oscillator,
which oscillates at the same frequency. This is the simplest method of metal detection. The main disadvantages of this circuit are the very poor sensitivity, especially for smaller metal objects, and the large temperature dependence of the oscillators. It is an obsolete circuit which is no longer used today. The detector requires some experience to operate, especially a sensitive ear capable of detecting even a small change in frequency.

2) Pulse inductive detector
This detector, unlike the other detectors, does not work on the principle of excitation of the coil by an oscillator, but excites the search coil by very short DC pulses. The search probe can consist of one or two coils, of which, when connected with one coil, the coil acts as both transmitter and receiver. In a two-coil arrangement, each coil performs a single function. First, the coil is in
transmitter mode, when a very short DC pulse is passed to it. Then the coil is switched to receiver mode, where the time of the transient on the coil is examined. If there is no metal in the coil's electromagnetic field, the response time of the coil is very short. If metal is present in the electromagnetic field, the coil response time is longer. This is evaluated by the evaluation unit as the presence of metal. The whole process repeats periodically at a rate of approximately 5,000 times per second. The main advantage of this detector is the ability to detect objects at greater depths. Resistance to interference The ability to detect objects in challenging soil conditions such as highly mineralized soil and saltwater-soaked sea beaches.
Disadvantages: poorly implemented metal discrimination, detectors operate exclusively in motion mode.

Example of the GPX 5000 PI detector, which can also discriminate ferrous objects
3)Inductive balance detector (VLF detectors)
I decided to build this detector in my work mainly because of the good metal resolution and because of the excellent range. It is the most widely used metal detection system today. This metal detection system is characterized by high stability and due to good metal resolution it is most suitable for use in our conditions. The detector works using two coils, one transmitting and the other receiving, which are compensated for each other so that they have zero inductance. The transmitting
coil is part of a simple oscillator which produces a sinusoidal signal of the largest possible amplitude. The receiving coil is balanced exactly with the transmitting coil so that the coils have zero inductance with respect to each other, so that there is no induced voltage on the receiving coil at rest. The presence of metal in the electromagnetic field of the coils disturbs the balance and the detector evaluates this change as a signal. The phase shift on the receiving coil can be used to approximately determine the type of metal detected. These detectors have a high sensitivity even for very small objects and a very accurate metal resolution with the possibility of detecting selected metal objects. The disadvantage is the very complex mutual adjustment of the coil array to make it mechanically and temperature resistant. The fabricated coil is very mechanically susceptible to impacts. Any deformation of one of the coils results in a disturbance of their mutual balancebalance and thus unbalance the coil, which has a negative effect on
range and overall detector function. The range of the detector is highly dependent on the precise balance of the coil array.
Therefore, the manufacture of coils is a relatively complicated process with a large amount of manual labor, which will be reflected in the cost of new probes. For cheaper detectors, a new probe is 1/2 the price of the instrument.
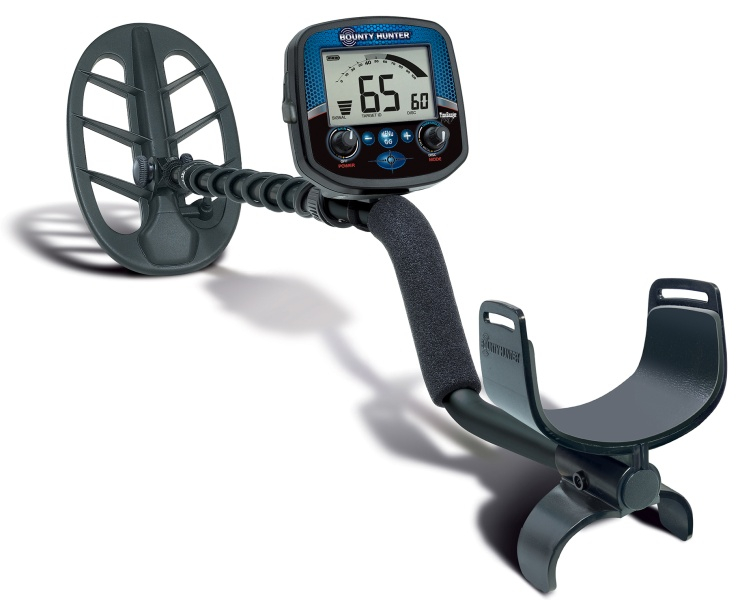

Time Ranger Pro detector is an example of advanced VLF detectors of today
4)Multifrequency metal detectors.
The great growth of microprocessors and the advancement of digital technology in signal processing has given rise to a new separate new group under the classical VLF detectors as their youngest development stage, namely multifrequency detectors. This is principally a VLF detector with the difference that on the transmitting coil you will no longer find a classical sine wave of one frequency but a sophisticated signal containing frequency components of different frequencies e.g. Such a detector then basically behaves like several single-frequency detectors with different frequency components. The resulting single frequency response measurements and final comparison will provide a sense of thely much more information (X number of frequencies) than with a single frequency detector where you have only one piece of information.
E.g. if the detector measures the lowest response at high frequencies,while low frequencies the target is almost invisibleit can expect that the target will probably be very small, which it will take into account when calculating the resulting object ID.
With a single frequency detector you only have one piece of information (either the target is visible or not) and nothing to compare it to. You would achieve a similar effect if you tried to detect the same target with several single frequency detectors of different frequencies, and then compare and average the results and IDs. For this reason, multi-frequency detectors that are capable of operating over a wide range of frequencies can cover a wide range of targets of all sizes. This eliminates the need to select the correct frequency for a given target type as with a single frequency detector. Also, by comparing the response from single frequencies, the target evaluation and detector operation in more difficult ground conditions is significantly improved.

Currently the best selling multi-frequency detector is the Minelab Equinox 800. Multi-frequency technology is used today by Minelab and Garrett.
For the more technically minded, a comparison of single frequency and multi-frequency detectors
The article is included in categories:
- Archive of articles > Metal Detectors - Reviews and Tests
- Archive of articles > Tutorials and History Hunters Magazine > Search instructions
Post
Dík za poučné čtení. 
Cenné informace, díky.
Poprosím místní "odborníky"ať si ujasní objasní základní pravidlo k používání VYSOKÝCH FREKVENCÍCH A MINERALIZACE
Psáno:Vysoké frekvence jsou doporučeny na silně mineralizovaných půdách ......
Řečeno:.........tím horší odolnost vůči mineralizaci........
Psáno zde:odstavec frekvence www.lovecpokladu.cz/home/test-sest-dni-s-detektorem-kovu-mars-gauss-trnitou-cestou-k-vrelemu-pratelstvi-8265
Řečeno:v čase cca.9:23
https://youtu.be/CdnjWwTxiMA
Jackart-Děkuji za upozornění ,ano máš pravdu.
Logicky vyšší frekvence citlivější na drobnější cíle jsou náchylnější na mineralizaci .( správně je to ve videu které jsem dělal)
Článěk z kterého je mylná informace je recenze na Gausse kterou jsem nepsal já.
Tenkrát když přišel prototypovej detektor tak se poslal několika hledačům (přihlásit se tenkrát mohl každý kdo měl myslím už nějakou dobu učet na LP ).Tento konkrétní psal GM4.
Každopádně bych řekl že to z jeho strany bude nějaký překlep, když člověk píše delší text snadno se tam chybička stylu zvýší/sníží snadno vloudí.
GM4 považuji za relativně zkušeného hledače takže bych řekl že to bude jen překlep.
Každopádně smekám před bystrostí oka a díky za upozornění.
P.Z.
Jako vždy, zajímavé a profesionální vysvětlení funkce detektorů podle konstrukce. Také jediná firma, které se dá plně věřit a ví dobře, o čem je řeč. Chválím a děkuji ! 
Dotaz k té mineralizaci. U Equinoxe je vyšší mineralizace GB >50? A znamená to tedy, že při vyšší mineralizaci půdy budou lépe pracovat jedničkové programy Park1 a Pole1? Že budou stabilnější a půjdou trochu hlouběji? Chápu to správně?
Steyer-ano v horsich pudnich podminkach lepe pracuji jednickove programy.Obecne na 95%lokalit se hodi spis jednickove programy.S dvojkama beres akorat zbytecne male cile coz je akorat na obtiz,blbe se to dohledava,zvednes civku o centimetr a cil zmizi a hlavne se tim zbytecne zdrzujes misto toho aby jsi kopal prespektivenjsi cile 
Steyer-ano v horsich pudnich podminkach lepe pracuji jednickove programy.Obecne na 95%lokalit se hodi spis jednickove programy.S dvojkama beres akorat zbytecne male cile coz je akorat na obtiz,blbe se to dohledava,zvednes civku o centimetr a cil zmizi a hlavne se tim zbytecne zdrzujes misto toho aby jsi kopal prespektivenjsi cile 
Jasné, díky.
K té mineralizaci u equinoxe na čedič je lepší program : pláž2
PT92....
To je hrozně obecnej a zároveň težkej dotaz protože záleží dost na charakteru té půdy , čedič to tahá spíš do železa , kdežto slanou vodu detektor zase bere jako barvu...
Stejně jako u slané vody můžeš mít množství soli ve vodě všude jiné a někde bude stačit klidně i pláž 1 i pod vodou a někde to zase bude prosolené že budeš muset mít pláž2 se sníženou citlivostí, tak stejné je to s čedičem, někde je ho málo a někde je to totální průser....
V takovejch podmínkách je prostě nejlepší to vyzkoušet a vzít si nějakej cíl , zakopat a protestovat kde to vyjde nejlépe a u toho se průběžně dívat jak vychází nastavení země.
PT92 Nesouhlasím...Jsem z kraje kde je mraky čediče a chodim do tech lokalit a 1 programy jsou top.. 
Pardon zapomněl jsem dodat že na čedič jsem šel s malou eliptickou cívkou.